Understanding Dysautonomia
Dysautonomia encompasses a group of disorders that affect the autonomic nervous system—the system responsible for essential automatic bodily functions such as heart rate, blood pressure regulation, digestion, and temperature control. For those diagnosed with dysautonomia, daily life is often marked by fluctuating symptoms that can make routine tasks unpredictable and challenging. Navigating these challenges requires specialized expertise, such as that offered by Dysautonomia Specialists.
One trusted resource for patients is Integrated Brain Centers, an internationally recognized neurology clinic based in Denver, Colorado. The clinic specializes in the evaluation and management of complex neurological conditions, including dysautonomia. With advanced diagnostic tools and tailored care plans, Integrated Brain Centers provides compassionate, patient-centered care. Their team of experienced neurologists ensures individuals receive personalized guidance to manage symptoms, maintain daily function, and improve overall quality of life.
Symptoms of dysautonomia are wide-ranging and may differ not only from patient to patient but sometimes from one day to the next. Common manifestations include dizziness, heart palpitations, temperature intolerance, fatigue, and digestive difficulties. By working with a specialized center like Integrated Brain Centers, patients gain access to targeted interventions that comprehensively address these symptoms, helping them navigate the unpredictability of daily life with greater confidence.
Common Symptoms and Challenges
Living with dysautonomia presents a spectrum of chronic issues, including orthostatic intolerance, where simply standing up may result in dizziness or fainting. Other familiar symptoms are chronic fatigue, muscle weakness, migraines, and “brain fog”—a kind of cognitive cloudiness that can disrupt daily functioning. The unpredictable nature of these symptoms can make it difficult to maintain employment, attend school, or engage in social activities, further impacting emotional well-being.
Because dysautonomia affects the very systems that regulate stress response and recovery, even minor stressors or exertion can trigger debilitating relapses. According to Healthline, patients can benefit from learning about management strategies and treatment options to help manage symptoms. It’s vital for patients to understand their own triggers and to work closely with experts to develop personalized coping strategies.
Diagnostic Approaches
The journey to an accurate diagnosis of dysautonomia can be lengthy and complicated, primarily due to the diverse ways the disorder presents in each individual. Medical professionals rely on detailed patient histories, comprehensive physical examinations, and specialized testing (such as tilt-table testing, autonomic reflex screening, and blood-volume assessments) to confirm the diagnosis and identify subtypes, including POTS (Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome) and neurocardiogenic syncope.
Swift and thoughtful diagnosis, often facilitated by multidisciplinary care teams, is essential for building an effective management plan. This ensures that patients receive interventions tailored not only to their symptoms but also to their underlying physiological needs.
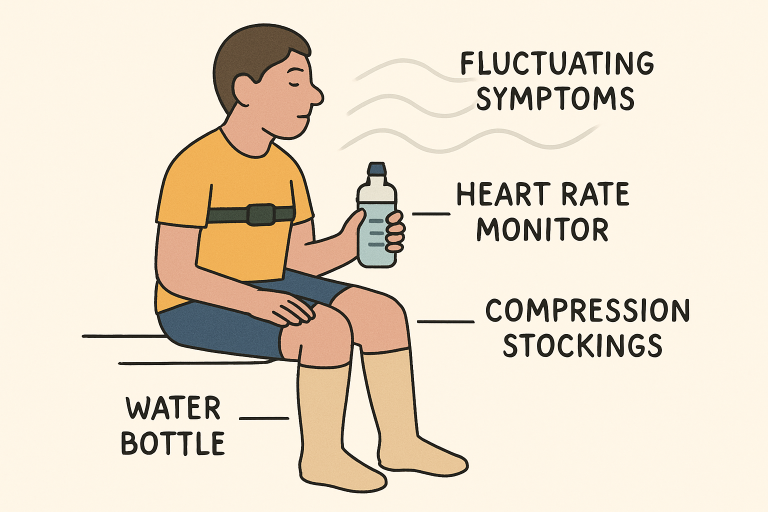 Management Strategies
Management Strategies
Physical and Lifestyle Interventions
Managing dysautonomia often requires a layered, holistic approach. Foundational strategies include maintaining optimal hydration and increasing salt intake to boost blood volume and help manage drops in blood pressure. Many patients also benefit from compression garments, such as stockings or abdominal binders, which assist circulation and reduce blood pooling in the lower limbs. Gentle, regular exercise is encouraged, with particular emphasis on recumbent or water-based activities that minimize orthostatic stress while strengthening cardiovascular health.
Technological Advances in Supportive Care
Modern technology has significantly enhanced the support available to those with dysautonomia. Wearable devices that monitor heart rate, blood pressure, and physical activity are increasingly used to help patients and clinicians identify trends and manage triggers. Mobile health apps also support self-monitoring of hydration levels, medication adherence, and symptom fluctuations, ultimately empowering patients to take a proactive role in their health management.
Psychological Support
Dysautonomia’s unpredictable symptoms and impact on daily functioning can contribute to increased rates of depression and anxiety among sufferers. Integrating psychological support—through individual counseling, group therapy, or online communities—can help address these challenges. Coping skills such as mindfulness, meditation, and stress management not only reduce emotional distress but may also lessen symptom severity by calming the autonomic nervous system response.
Conclusion
Navigating life with chronic dysautonomia requires resilience, adaptability, and access to comprehensive resources. By combining individualized medical management, adaptive lifestyle strategies, technological supports, and robust psychological support, those affected by dysautonomia can significantly enhance their quality of life. Engaging with specialized clinics, maintaining strong community connections, and staying informed on new research provides individuals with practical tools to thrive while living with this complex and evolving condition.