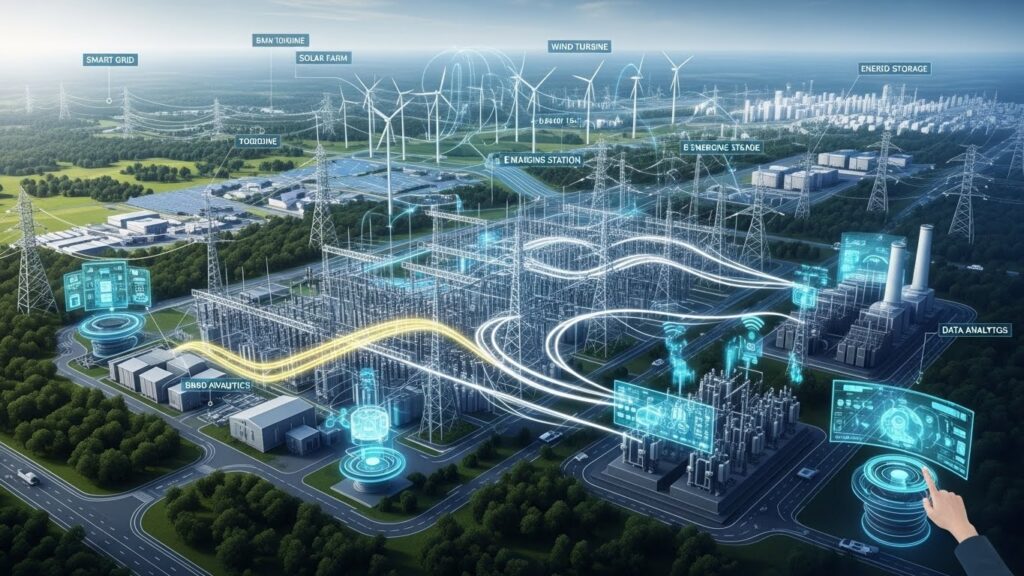
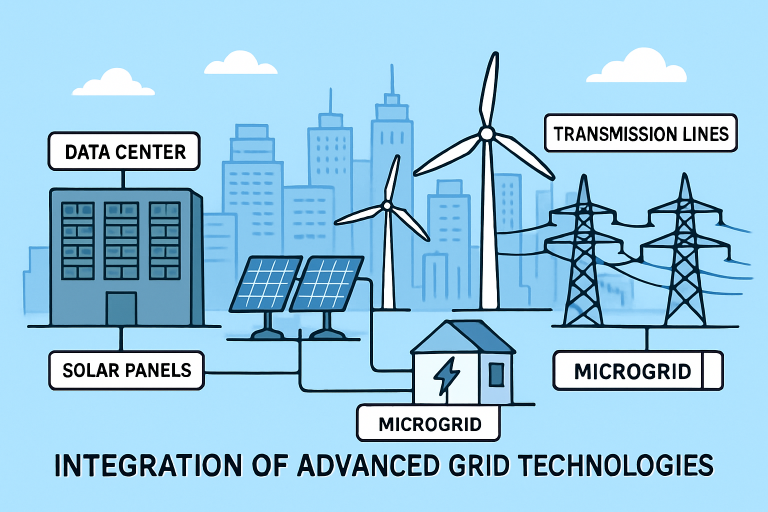
As the world experiences rapid electrification across industries and communities, the need for resilient, adaptable, and efficient power distribution systems continues to rise. With increased dependence on digital technology, urbanization, and sustainable energy, the evolution of infrastructure necessitates innovative solutions that address both the growing demand and emerging challenges. Leading advancements such as microgrids, HVDC transmission, and smart grid technologies are transforming how we transmit and manage electricity. Components like dry type transformers play a vital role in this transformation, supporting safe and efficient voltage regulation within next-generation systems.
Power distribution is evolving beyond reliability, focusing on agility to handle variable loads, integrate renewable energy sources, and rapidly recover from disruptions. Influenced by extreme weather, data demands, and decarbonization goals, modern grids require advanced components and a holistic approach. The integration of traditional and innovative technologies, such as power electronics and energy storage, is crucial for efficient energy management. Tailored strategies for urban, industrial, and rural settings are essential, emphasizing rapid adaptability and the blend of digital intelligence with resilient infrastructure. Collaboration among governments, utilities, and industry aims to establish standards and promote technologies that ensure sustainability and promote economic growth, thereby reshaping modern infrastructure expectations.
 High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Systems
High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Systems
Data centers, which serve as the backbone of the digital economy, are experiencing exponential growth in power consumption due to the rise of artificial intelligence and cloud computing. Traditional 48-volt power distribution systems are reaching their limits in such high-density environments. In response, major players like NVIDIA are implementing 800V high-voltage direct current (HVDC) systems, which dramatically increase efficiency by reducing current requirements and transmission losses. This allows for longer cable runs, more scalable infrastructure, and a significant reduction in energy waste—all of which are essential for the world’s most demanding computing workloads.
Aside from operational benefits, HVDC systems also facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources and cross-border electricity trade, enhancing both grid stability and international cooperation. The shift towards HVDC represents a leap not just in efficiency but in how future data- and energy-intensive facilities around the globe will be engineered.
The Rise of Microgrids
Microgrids are emerging as vital tools for localized energy management, combining on-site generation, storage, and load optimization. Their greatest strength lies in their ability to operate independently (or “islanded”) from the primary utility grid, providing backup power during outages and supporting critical infrastructure. As of 2025, U.S. microgrid capacity is estimated to approach 10 GW, a dramatic rise from 4.4 GW just a few years prior. This growth reflects the dual drivers of climate resilience and sustainability—especially as extreme weather strains traditional grid models.
From healthcare campuses to remote communities and urban neighborhoods, microgrids enhance resilience, reduce energy costs, and facilitate the achievement of renewable energy targets. Large tech companies and utilities are both investing heavily to ensure energy security and operational continuity. According to Reuters, this momentum is expected to accelerate, particularly as distributed energy resources become more affordable and regulations catch up with technological advancements.
Advancements in Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grids incorporate advanced digital communication, sensors, and automation to monitor electricity demand, prevent overloads, and integrate renewable generation with unprecedented sophistication. These real-time insights enable utilities to optimize supply, respond dynamically to market or weather changes, and engage in predictive maintenance, all of which enhance overall reliability and economic efficiency.
Digital Systems and Renewables Integration
One of the most significant benefits of smart grids is the seamless integration of distributed energy resources—such as solar, wind, and batteries—into utility grids that once relied on steady, centralized generation. Automated systems and sophisticated cybersecurity safeguards are crucial, as are global standards prescribed by leaders such as IEEE’s Smart Grid initiatives.
Policy and Investment in Grid Modernization
Recognizing the urgent need for a resilient electrical infrastructure, the U.S. government has committed over $ 36.9 billion to modernize and secure the power grid, with approximately $ 7.6 billion allocated under the Grid Resilience and Innovation Partnerships (GRIP) program. These investments aim to expand transmission capacity, upgrade infrastructure, and integrate renewable energy sources, thereby significantly reducing outage durations and frequencies. The strategy includes funding for advanced grid controls and smart-grid technologies, emphasizing the importance of federal leadership and public investment in fostering private innovation for a cleaner, more resilient energy future.
Future Outlook
The road ahead in power distribution promises both significant opportunities and steep challenges. Pioneering technologies, such as HVDC, microgrids, and intelligent grid systems—supported by robust government investment and evolving standards—are reshaping the global energy network. These solutions offer not only higher efficiency and reliability but also the flexibility to adapt to changing social, economic, and environmental requirements.
Ultimately, the collaboration between utilities, private industry, policymakers, and communities will determine how quickly and effectively these innovations become standard practice. By prioritizing adaptability, sustainability, and wise investments, modern infrastructure will rise to meet the complex demands of our electrified future—delivering power where and when it’s needed most.