Digital images surround us in every aspect of our lives. From social media to professional presentations, they play a crucial role in how we communicate and express ideas visually. But have you ever wondered what really lies beneath the surface of those vibrant pictures? Enter bit planes—a fascinating concept that can unlock the secrets behind digital imagery.
Bit planes are fundamental building blocks that help define how colors and details come together in an image. Understanding them not only enhances your appreciation for digital art but also equips you with knowledge applicable across various tech fields. Whether you’re a budding photographer or someone curious about how computers process visuals, exploring bit planes will elevate your understanding of digital imaging to new heights. Let’s dive into this captivating world!
What are Bit Planes?
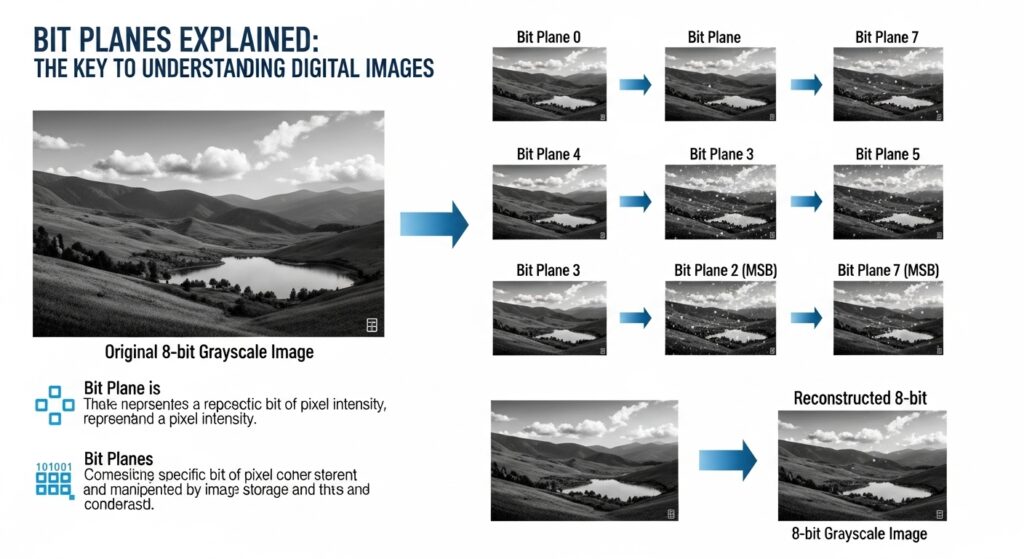
Bit planes are layers that represent the individual bits of pixel data in a digital image. Each bit plane corresponds to a specific level of brightness or color intensity within an image.
For instance, in an 8-bit grayscale image, there are eight bit planes. The first plane might encode the darkest pixels, while the last one captures the brightest. This layered approach allows for easier manipulation and analysis of visual information.
When combined, these planes produce the full spectrum of colors we see on our screens. In more complex images like RGB formats, multiple bit planes exist for each color channel—red, green, and blue—each contributing to the final visual output.
Understanding bit planes is essential for tasks such as compression and filtering since they allow developers to isolate certain features without affecting others in a digital image.
How do Bit Planes Work?
Bit planes operate by breaking down a digital image into its individual bits. Each bit represents a specific level of brightness or color within the image. This segmentation allows for clearer manipulation of the data.
For an 8-bit grayscale image, for instance, there are eight distinct layers—one for each bit. The first layer captures the darkest pixel values, while subsequent layers represent progressively lighter shades. By isolating these layers, you can analyze and modify them independently.
When combined back together, all these bit planes reconstruct the complete image in a way that highlights details not easily seen when viewing the whole picture at once. This layered approach provides flexibility in various applications like compression and filtering.
Understanding how these planes interrelate enhances our grasp of digital imagery’s complexities and opens doors to innovative editing techniques.
The Importance of Bit Depth in Digital Images
Bit depth is a crucial aspect of digital images that determines the range of colors and tonal values they can represent. It refers to the number of bits used for each pixel in an image. Higher bit depth means more possible colors, leading to finer gradients and smoother transitions.
For instance, an 8-bit image can display 256 colors, while a 16-bit image boasts over 65,000 shades per channel. This difference significantly impacts how images are perceived. Photographers and graphic designers often prefer higher bit depths for their ability to capture subtle variations.
In applications like medical imaging or professional photography, precise color representation is essential. A broader palette allows for enhanced detail and clarity, making it easier to differentiate between similar hues or tones.
Understanding bit depth helps artists choose the right format for their projects, ensuring visual fidelity remains intact throughout editing and output processes.
Applications of Bit Planes
Bit planes find their utility across various fields, enhancing the way we process and analyze digital images. One prominent application is in image compression. By isolating significant data from less important bits, compression algorithms can reduce file sizes without sacrificing quality.
In medical imaging, bit planes play a critical role. They help visualize multi-layered scans like MRI or CT images by allowing radiologists to focus on specific tissue types or anomalies through layer manipulation.
Another interesting use lies in computer vision. Bit plane analysis aids object recognition and segmentation tasks by providing clearer insights into pixel-level details. This granular approach improves machine learning model performance.
Furthermore, video encoding technologies leverage bit planes for more efficient streaming and storage solutions, ensuring high-quality playback even on limited bandwidth connections.
How to Create and Manipulate Bit Planes
Creating and manipulating bit planes involves a few straightforward steps. First, you need to understand the image’s pixel representation. Each pixel is usually made up of multiple bits depending on the color depth.
To extract bit planes, start by isolating each individual bit from your image data. This can be done using programming languages like Python or MATLAB, where you can use bitwise operations to separate them.
Once you’ve extracted the planes, manipulation becomes possible. For instance, you might want to enhance contrast by adjusting specific bits or combining different planes for creative results.
Visualizing these changes helps in understanding their impact on the overall image quality. Tools like OpenCV provide functions that facilitate both extraction and modification seamlessly.
Experimenting with various methods allows for unique transformations that may enhance images in unexpected ways.
Challenges and Limitations of Bit Planes
Bit planes play a crucial role in image representation, but they come with their own set of challenges. One significant limitation is the increased data size associated with higher bit depths. This results in larger files that can slow down processing and storage.
Another challenge arises when manipulating bit planes during editing or compression. Changes made to one plane can inadvertently affect others, leading to unexpected outcomes. This complexity demands careful handling from software developers and users alike.
Additionally, not all imaging systems fully support bit planes, which could hinder compatibility across different platforms. As technology advances, maintaining uniformity becomes increasingly difficult.
Color banding is another concern tied to lower bit depths. It reduces the smoothness of color transitions, creating an unsightly appearance in images that require fine detail. Understanding these limitations helps users navigate potential pitfalls when working with digital imagery.
Conclusion
Understanding bit planes is essential for anyone delving into the world of digital images. These layers, representing different bits of information, play a crucial role in how images are stored and processed. By grasping how they work, you gain insights into image quality and manipulation techniques.
The significance of bit depth cannot be overstated. It directly influences the range of colors that can be represented within an image. Whether you’re working on graphic design projects or exploring computer vision applications, knowing about bit planes helps elevate your understanding.
While there are challenges associated with using bit planes—such as increased storage requirements and processing complexity—their advantages far outweigh these limitations when handled correctly. They provide flexibility in image analysis and enhancement.
From creating unique visual effects to analyzing complex data sets, mastering bit planes opens doors to innovative applications in various fields like graphic design, medical imaging, and machine learning algorithms. Embracing this knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional in the industry.
Bit planes offer fascinating insights into digital imagery’s foundation while presenting numerous opportunities for creativity and exploration.